Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin Heilongjiang 150001, P. R. China
2 Department of Bioengineering, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA
The synthetic aperture-based linear-array photoacoustic tomography (PAT) was proposed to address the limited-view shortcomings of the single aperture, but the detection field of view (FOV) determined by the aperture orientation effect was not fully considered yet, leading to the limited-view observation and image resolution degradation. Herein, the aperture orientation effect was proposed from the theoretical model and then it was verified via both the numerical simulation and phantom experiment. Different orientations were enumerated sequentially in the simulation to approximate the ideal full-view case for the optimal detection FOV, considering the detection pattern of the linear-array transducer. As a result, the corresponding optimal aperture orientation was 60� if the synthetic aperture was seamlessly established by three single linear arrays, where the overlapped detection pattern was optimized from the individual linear-array transducer at the adjacent positions. Therefore, the limited-view artifacts were minimized and the image resolution was enhanced in this aperture orientation. This study showed that the aperture orientation had great influence on the optimal detection FOV in the synthetic aperture configuration, where the full-view imaging quality and enhanced image resolution could be achieved.
Photoacoustic tomography synthetic aperture aperture orientation linear-array transducer Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2018, 11(4): 1850015
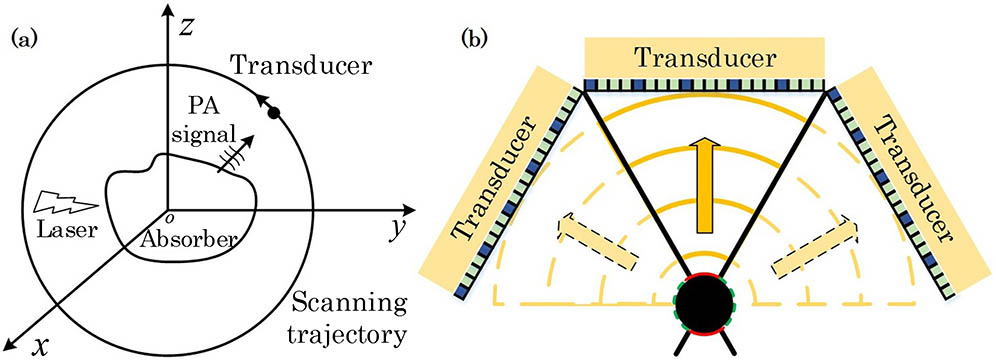
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Beijing 100039, China
3 Institute of Opto-electronics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) has the unique capability of visualizing optical absorption inside several centimeters-deep biological tissue with a high spatial resolution. However, single linear-array transducer-based PAT suffers from the limited-view challenge, and thus the synthetic aperture configuration is designed that still requires multichannel data acquisition hardware. Herein, a feasible synthetic aperture PAT based on compressed sensing reconstruction is proposed. Both the simulation and experimental results tested the theoretical model and validated that this approach can improve the image resolution and address the limited-view problem while preserving the target information with a fewer number of measurements.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 101102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Photoacoustic tomography is a noninvasive and nonionized biomedical imaging modality but it cannot reveal the inner structure and sideward boundary information of blood vessels in the linear array detection mode. In contrast, Monte Carlo (MC) light transport could provide the optical fluence distribution around the entire vascular area. This research explores the combination of linear array transducer-based photoacoustic tomography and MC light transport in the blood vessel quantification. Simulation, phantom, and in vivo experiments are in good correlation with the ultrasound imaging, validating this approach can clearly visualize the internal region of blood vessels from background tissue.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 111701





